BLOOD COMPONENTS (PLASMA, EXOSOMES)
We use original personalized cell preparations, young plasma, blood components, exosomes for the treatment of diseases and in anti-aging medicine.
Young blood plasma has a beneficial effect on various organs of mice. More than halving the epigenetic age of blood, heart, and liver tissue. A less pronounced, but statistically significant effect of rejuvenation can be observed in the hypothalamus. www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.07.082917v1.full.pdf
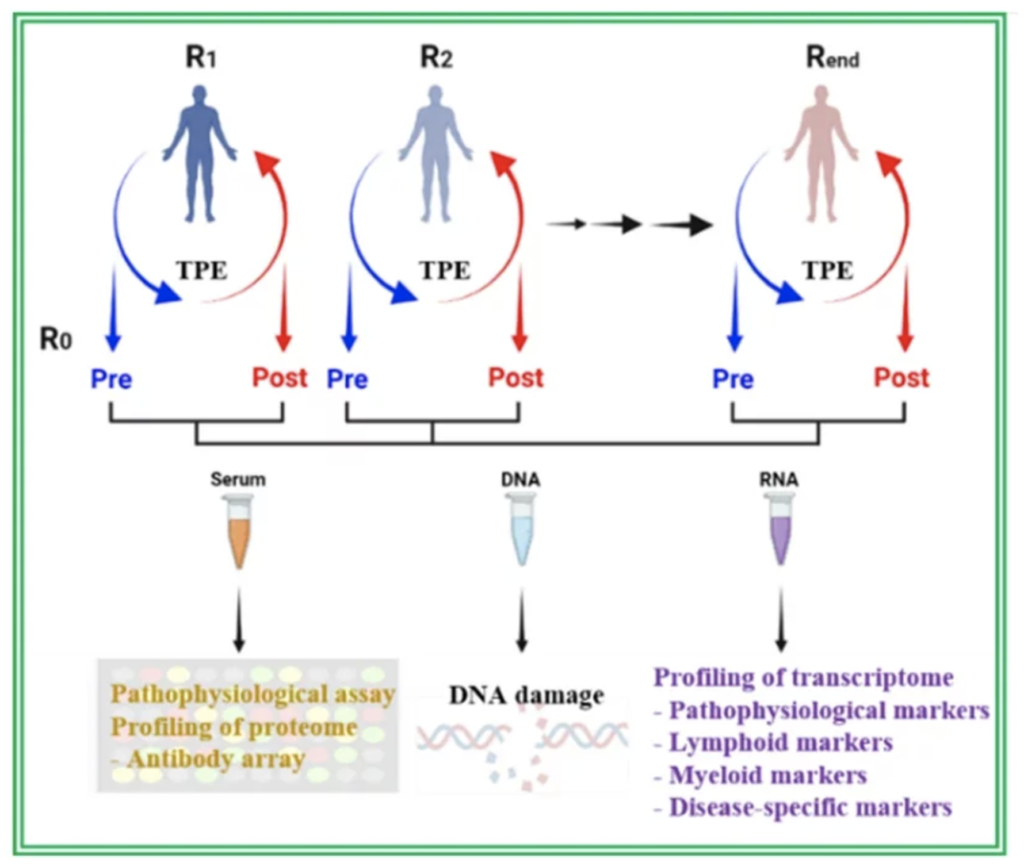
Altering therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE) to dilute systemic factors that become harmful when elevated with age can be a rapidly effective rejuvenation therapy that rewires important signaling pathways into adolescence. www.trasci.com/article/S1473-0502(21)00128-2/fulltext
The loss of gene expression with age is mimicked by parabiosis: aging blood reduces global gene expression, and young blood restores it in select cell types.
www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04461-2
Plasma from young rats transfused into old rats produces anti-aging effects.
www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/rej.2020.2354
Administration of cerebrospinal fluid from young mice to old mice restores memory recall in older animals by inducing the formation of a fatty myelin sheath that insulates neurons in the brain.
www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-00860-7
Donor blood transfusion can be an effective treatment for the consequences of a stroke.
www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-17930-x
EXOSOMES
Exosomes are taken up by distant cells, where they can influence cell function and behavior. Intercellular communication through exosomes is involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and inflammatory diseases.
EVs derived from stem cells perform the same functions as their parent cells. which may represent new therapeutic agents for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes mellitus T1D.
www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35095751/
An intercellular transfer of telomeres rescues T cells from senescence and promotes long-term immunological memory. www.nature.com/articles/s41556-022-00991-z
Human MSC exosomes reduce cellular senescence in renal epithelial cells. doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413562
Intranasal administration of exosomes has been recognized as an effective and reliable way to bypass the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and deliver drugs to the CNS. www.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/stem.3456
Cells in close proximity synchronize their differentiation stages and cellular phenotypes with each other through cellular communication mediated by extracellular vesicles (EV) vesicles—phenotypic cell synchrony (PSyC). PSyC is a new form of cell-to-cell communication mediated by the regulation of neighboring cells and may be widely involved in tissue development and homeostasis.
www.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jev2.12147
Inhalation of secretome and exosomes of lung spheroid cells promotes lung recovery in pulmonary fibrosis. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-14344-7
MSC-derivatives of EV are highly effective senotherapeutic agents that slow down the progression of aging and diseases caused by cell senescence. doi.org/10.1111/acel.13337
Dermal exosomes with miRNA promote hair regeneration.
www.advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/30/eaba1685
Rejuvenation of mesenchymal stem cells with extracellular vesicles suppresses the increase in the level of reactive oxygen species. www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-74444-8
FORMED BLOOD ELEMENTS
RBCs promote inflammation, serve as critical immune sensors through surface expression of the nucleic acid sensitive Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.abj1008
