STEM CELL THERAPY FOR DIABETES MELLITUS
We have many years of experience in treating type 1 diabetes mellitus and complications with stem cell therapy.
Surrogate β-cells can be obtained from various sources of stem cells. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) are widely available from several tissues, safe and well tolerated. MSCs can differentiate in vitro into insulin producing cells (IPCs). In experimental animals, the efficacy of PBMCs derived from human MSCs (hMSCs) in controlling chemically induced diabetes was comparable, if not better, to that of β-cells derived from pluripotent stem cells. An interesting feature of MSCs is their ability to evade immune recognition.
The age of the donor also affects the therapeutic potential of the obtained MSCs. The yield of hMSC obtained by bone marrow aspiration decreases with age. MSCs derived from younger individuals have a higher proliferation rate with lower levels of oxidative stress-mediated damage.
www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.690623/full
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) increases C-peptide levels and induces insulin independence in patients with type 1 diabetes.
www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00167/full
A meta-analysis confirmed the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. www.stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-021-02342-5#Abs1
Cord blood SCs promote the production of regulatory T cells, thereby reversing hyperglycemia in NOD mice. Patients with DM1 treated with cord blood SC also did not show any adverse reactions in the absence of a significant effect on glycometabolic control. Although hematopoietic SCs rarely revert hyperglycemia in NOD mice, they exhibit profound immunomodulatory properties in humans.
www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21862682/
Bone marrow and blood HSCs are altered in some autoimmune conditions such as T1DM and MS. Currently, HCS is expected to be considered as a new “biological drug” that can be personalized and modeled as a new topical therapeutic option in T1DM. www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.694118/full
MSC transplantation may be a useful treatment for both T1DM and T2DM. MSC transplantation in preclinical trials and clinical trials in T1DM and T2DM has shown moderate to significant improvement in diabetes without side effects. www.bmrat.org/index.php/BMRAT/article/view/144В
Interim results from a multicenter clinical trial demonstrate insulin secretion by implanted cells in patients with type 1 diabetes. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/12/211202113432.htm
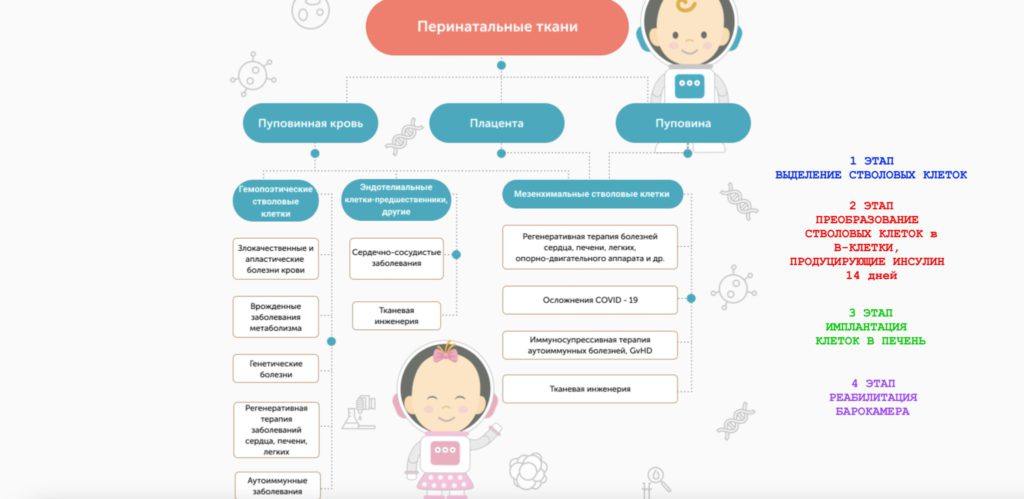
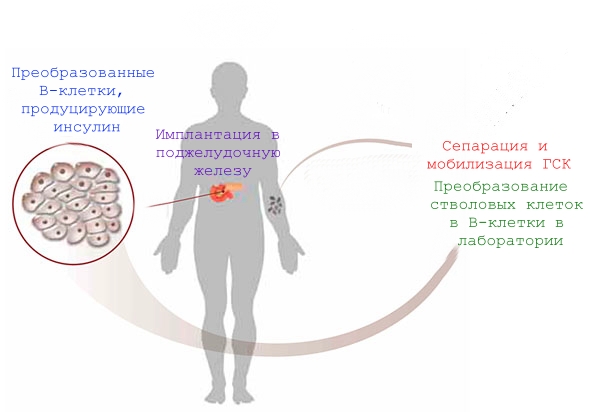
In different clinical cases, depending on the patient’s condition, immune system parameters, age, we use different cell technologies